CUET EXAM Chemistry Previous Year Questions Set 1
CUET Chemistry 2023 Set 1
(i) Silicon doped with electron elements of group-13 forms.
1. Conductor
2. Intrinsic semiconductor
3. p-type semi conductor
4. n-type semi conductor
Solution

(ii) Atoms of element B form hep lattice and those of the element
A occupy 2nd/3 of octahedral voids. What is the formula of the
compound formed by the element A and B?
1.A3B4
2.A4B3
3.AB
4.A4B
Solution

(iii) Which of the following is more reliable ?
1. % (w/v)
2. Molarity (M)
3. Molality (m)
4. Strength (S)
Solution
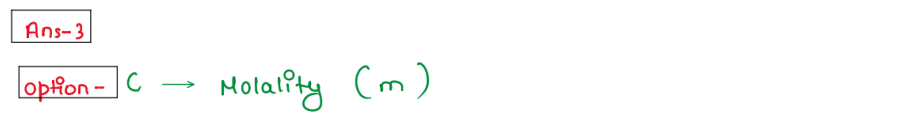
(iv) Calculate the mass of urea (NH2CONH2) required in making
2.5 kg of 0.25 molal aqueous solution.
1. 36.95g
2. 37.5g
3. 39g
4. 35.95g
Solution
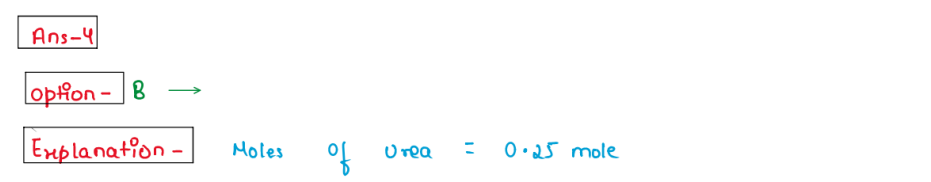

(v)
Solution

(vi)Decreasing order of reducing power of the given species as
per their standard reduction potential is:
A.-2.36
B. +0.54
C.+1.23
D.-0.74
E. +1.81
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A>D>E>B>C
2. A>D>B>C>E
3. EC>A>B>D
4. E>C>B>D>A
Solution

(vii) A solution of CuSO4 is electrolysed for 10 min with a current
of 1.5 A. What is the mass of copper deposited at the cathode (molar
mass of Cu=63g) (1F = 96487c).
1. 2.93 g
2. 3.4 g
3. 1.9 g
4. 0.2938 g
Solution
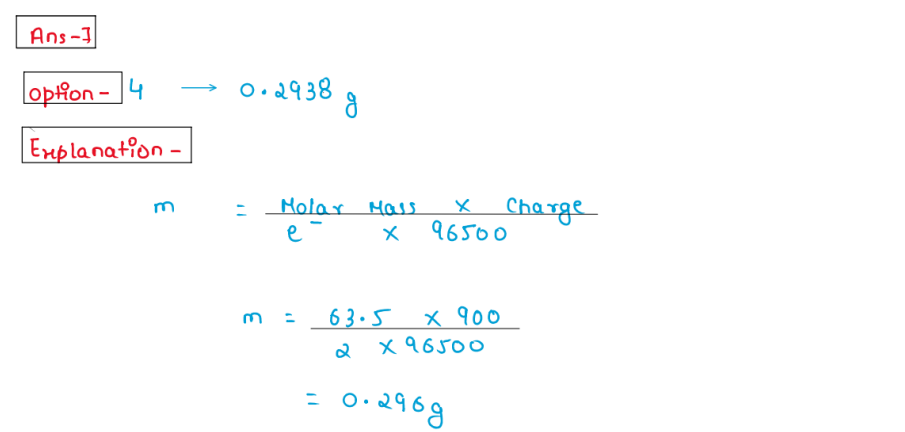
(viii) For the cell: Ni (s) | Ni2+ (0.1M) || Cu2+ 2+ (0.1M) | Cu(s) the
cell potential will increase when,
1. Ni2+ ion concentration is increased
2. Cu2+ ion concentration is decreased
3. Cu2+ ion concentration is increased
4. Temperature of the cell is decreased
Solution

(ix) A first order reaction is found to have a rate constant, k = 5.5 *
10 ^ - 14 * s ^ -1 Find the half life of the reaction.
1. t1/2 = 0.693s
2.t1/2=55*10^13 s
3.t1/2=2.303*10^13s
4.t1/6=1.26*10^13*s
Solution
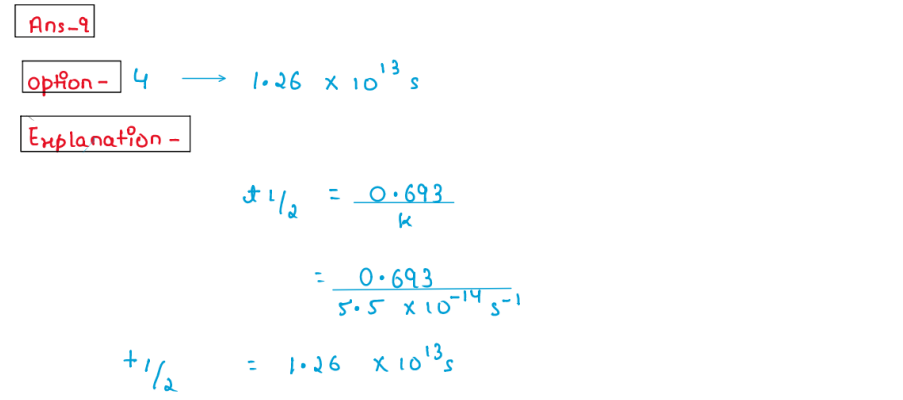
(x) In the below given hypothetical equation r = k[A] [B] If the
concentration of [B] is kept constant and concentration of [A] is
increased to 3 times, the reaction rate increases 27 times, then the
order of reaction with respect to A is:
1.3
2.2
3.1
4.0
Solution
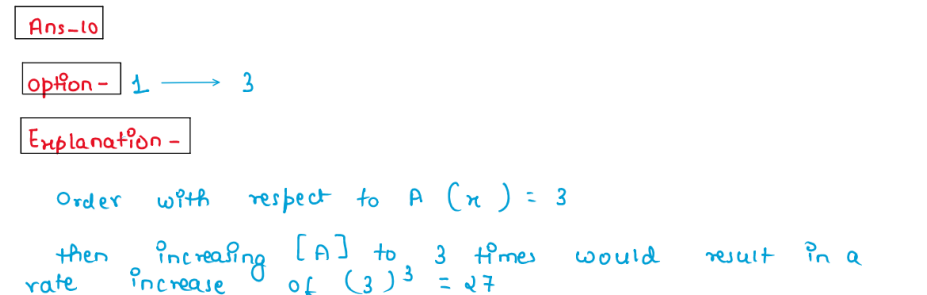
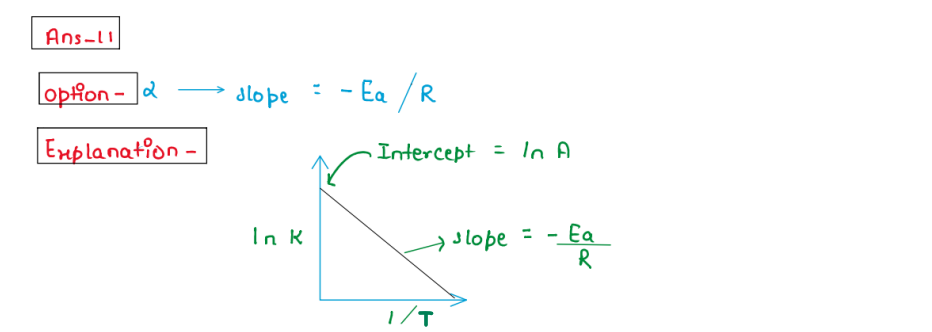
(xi) A graph is plotted between Ink and 1/T, what is the value of
slope?
1. Slope = Ea/ R
2. Slope = -Ea/R
3.Slope =k/R
4. Slope = -k/R
Solution


(xii) Ore of copper is:
1. Malachite
2. Magnetite
3. Cryolite
4. Calamine
Solution

(xiii) Zone refining is based on the principle that
1. Impurities of low boiling point metals can be separated by
distillation
2. Impurities are more soluble in molten metal than in solid metal
3. Vapours of volatile compounds can be decomposed to give pure
metal
4. Different component can be absorbed differently on a adsorbant
Solution

(xiv) The strongest oxidising and reducing agents respectively
are.
1.F2 and I-
2. Br2 and Cl-
3.Cl2and Br-
4.Cl2and I2
Solution

(xv) What is basicity of H3PO4
1. 1
2. 2
3. 3
4. 5
Solution

(xvi) Identify the correct statement(s).
A. Fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine.
B. Sulphur in vapour state shows paramagnetic behavior.
C. H2S is more acidic than H2Te.
D. Fluorine form two oxoacids HOF, HOFO.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A and B only
2.B and C only
3.A,B, C,D only
4. A and C only
Solution

(xvii) Which is best description of behavior of bromine in the
reaction given below?
H20 + Br2 —> HBr +HOBr
1. Proton accepted only
2. Both oxidised and Reduced
3. Oxidised only
4. Reduced only
Solution

(xviii) Which of the following ionic species has the greatest proton
affinity to form stable compound?
1. HS-
2. NH2-
3. F-
4. I-
Solution


(xix) Which one of the following characteristics of the transition
metals is associated with their catalytic property/activity?
1. colour of hydrated ion
2. variable oxidation states
3. high enthalpy of atomisation
4. paramagnetic behaviour
Solution

(xx) The aqueous solution containing which one of the following
ions will be colourless (Atomic number of Sc=21, Fe = 26, Ti = 22, Mn
= 25)
1. Sc3+
2. Fe2+
3. Ti3+
4. Mn2+
Solution

(xxi) Which of the complexes give white ppt when treated with
aqueous solution of BaCl2?
A. [Co(NH3)5S04]CI
B. [Co(NH3)3CI]1S04
C. [Co(NH3)5 (NO2)](NO2)2
D. [Co(NH3)5 CN] SO4
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. B, C only
2.B.D only
3. A, C only
4.A,C, D only
Solution


(xxii) The i
ncreasing order of magnetic behaviour for following
complex is
A. [Ti(H20)6]3+
B. [V(H20)6]3+
C. [MnCl4]2-
D. [MnF6]3-
E. [Cr(H20)6]3+
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A< B< C< D< E
2. E< D< C< B< A
3. D< A< B< C< E
4. A< B< E< D< C
Solution

(xxiii) Grignard reagent should be prepared under anhydrous
condition because
1. carbon Mg bond is not highly polar
2. Mg-X bond is essentially covalent
3. It reacts with proton of water to form HX
4. It reacts with H.O to form alkane
Solution
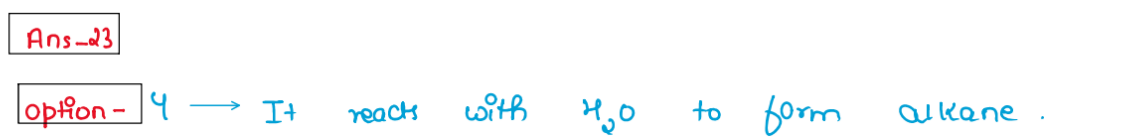
(xxiv) What will be the product of the following reaction: C6H5ONa + C2H5Cl→? 1. C6H5COC2H5 2. C6H5OC2H5 3. C6H5OC2H4Cl 4. C2H5OC2H6
Solution


(xxv) Allyl chloride on dehydrochlorination gives:
1. Propadiene
2. Propylene
3. Alkyl alcohol
4. Acetyl chloride
Solution


(xxvi) Arrange the following sets of compounds in order of their increasing boiling points. A. Pentan-1-ol B. Butan-1-ol C. Butan-2-ol D. Ethanol E. Propan-1-ol Choose the correct answer from the options given below: 1. A< B< C< D< E 2. B< C< D< E< A 3. C< D< E< A< B 4. D< E< C< B< A
Solution
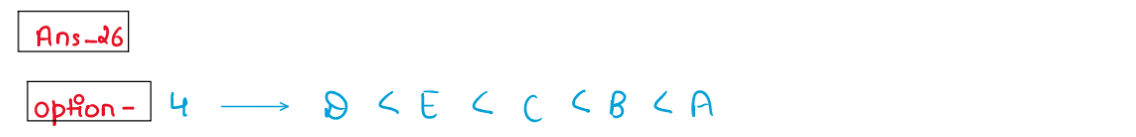
(xxvii) Monochlorination of toulene in sunlight followed by
hydrolysis with aq NaOH yields.
1. o-Cresol
2. m-Cresol
3. 2,4-Dihydroxytoulene
4. Benzylalcohal
Solution


(xxviii) When phenol is treated with chloroform in the presence of
NaOH, the major product formed is ?
1. 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid
2. Anisole
3. Salicyaldehyde
4. Methoxytoluene
Solution


(xxix) Reaction of nitrous acid with aliphatic primary amine in cold
gives.
1. A diazonium salt
2. An alcohol
3. A nitrite
4. A dye
Solution
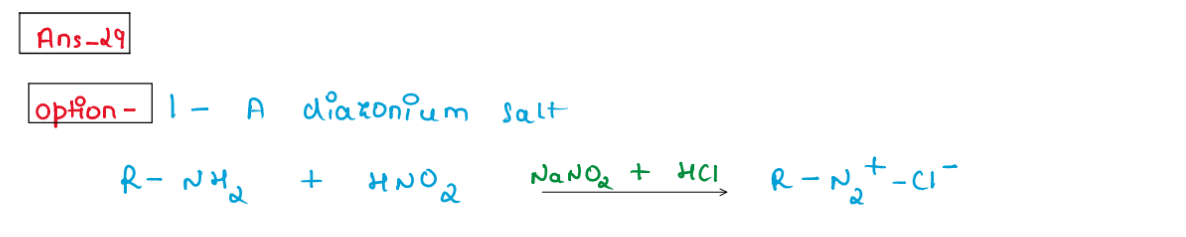
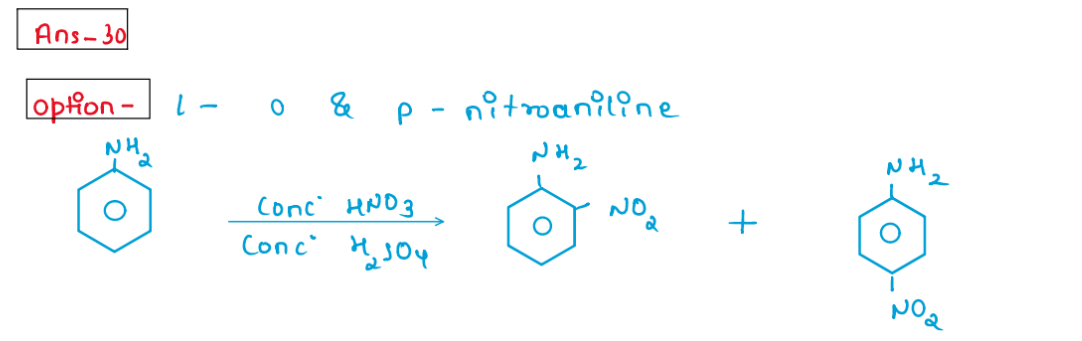
(xxx) Aniline upon heating with conc. HNO3 and concentrated H2S04 mixture gives. 1. o- and p-nitroaniline 2. o-Nitroaniline 3. Black terry mass 4. 2,4,6-trinitroaniline
Solution
(xxxi) Which of the following will not be sweet in taste?
1. Maltose
2. Glycogen
3. Lactose
4. Fructose
Solution

(xxxii) Which of the following will act as antiseptic as well as
disinfectant?
1. Boric acid
2. Iodoform
3. Sulphur dioxide
4. Phenol
Solution

(xxxiii) Bredig's arc method is.
1. To coagulate colloidal sol
2. To prepare colloidal sol
3. To purify the colloidal sol
4. To prepare the micelles
Solution


(xxxiv) The formation of micelles takes place.
1. Only above a particular temperature and above a particular
concentration
2. Only below a particular temperature and below a particular
concentration
3. Only above Kraft temperature and below CMC
4. Only below Kraft temperature and above CMC
Solution

(xxxv) The Arseneous sulphide As2S3 sol has negative (-) charge.
The maximum power to precipiate it is of:
1. H28O4
2. Na3PO4
3. CaCl2
4. AlCl3
Solution





 Free Mock Test Papers
Free Mock Test Papers